POLI 144AB Coding Workshop 3
7 minute read
library(tidyverse)
Introduction
Linear regression is a fundamental statistical method used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. In this lesson, we will cover the basics of linear regression, including how to implement it in R.
What is Linear Regression?
Linear regression aims to find the best-fitting straight line through the data points, predicting the dependent variable (Y) from the independent variable(s) (X).
Simple Linear Regression
Simple linear regression involves one dependent variable and one independent variable. The model is represented as:
\[Y = \beta_0 + \beta_1X + \epsilon\]- $Y$ is the dependent variable.
- $X$ is the independent variable.
- $\beta_0$ is the intercept.
- $\beta_1$ is the slope of the line.
- $\epsilon$ is the error term.
Dataset
For this lesson, we’ll use the mtcars dataset available in R.
# Load the dataset
data(mtcars)
force(mtcars)
## mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
## Mazda RX4 21.0 6 160.0 110 3.90 2.620 16.46 0 1 4 4
## Mazda RX4 Wag 21.0 6 160.0 110 3.90 2.875 17.02 0 1 4 4
## Datsun 710 22.8 4 108.0 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1 4 1
## Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 6 258.0 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0 3 1
## Hornet Sportabout 18.7 8 360.0 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0 0 3 2
## Valiant 18.1 6 225.0 105 2.76 3.460 20.22 1 0 3 1
## Duster 360 14.3 8 360.0 245 3.21 3.570 15.84 0 0 3 4
## Merc 240D 24.4 4 146.7 62 3.69 3.190 20.00 1 0 4 2
## Merc 230 22.8 4 140.8 95 3.92 3.150 22.90 1 0 4 2
## Merc 280 19.2 6 167.6 123 3.92 3.440 18.30 1 0 4 4
## Merc 280C 17.8 6 167.6 123 3.92 3.440 18.90 1 0 4 4
## Merc 450SE 16.4 8 275.8 180 3.07 4.070 17.40 0 0 3 3
## Merc 450SL 17.3 8 275.8 180 3.07 3.730 17.60 0 0 3 3
## Merc 450SLC 15.2 8 275.8 180 3.07 3.780 18.00 0 0 3 3
## Cadillac Fleetwood 10.4 8 472.0 205 2.93 5.250 17.98 0 0 3 4
## Lincoln Continental 10.4 8 460.0 215 3.00 5.424 17.82 0 0 3 4
## Chrysler Imperial 14.7 8 440.0 230 3.23 5.345 17.42 0 0 3 4
## Fiat 128 32.4 4 78.7 66 4.08 2.200 19.47 1 1 4 1
## Honda Civic 30.4 4 75.7 52 4.93 1.615 18.52 1 1 4 2
## Toyota Corolla 33.9 4 71.1 65 4.22 1.835 19.90 1 1 4 1
## Toyota Corona 21.5 4 120.1 97 3.70 2.465 20.01 1 0 3 1
## Dodge Challenger 15.5 8 318.0 150 2.76 3.520 16.87 0 0 3 2
## AMC Javelin 15.2 8 304.0 150 3.15 3.435 17.30 0 0 3 2
## Camaro Z28 13.3 8 350.0 245 3.73 3.840 15.41 0 0 3 4
## Pontiac Firebird 19.2 8 400.0 175 3.08 3.845 17.05 0 0 3 2
## Fiat X1-9 27.3 4 79.0 66 4.08 1.935 18.90 1 1 4 1
## Porsche 914-2 26.0 4 120.3 91 4.43 2.140 16.70 0 1 5 2
## Lotus Europa 30.4 4 95.1 113 3.77 1.513 16.90 1 1 5 2
## Ford Pantera L 15.8 8 351.0 264 4.22 3.170 14.50 0 1 5 4
## Ferrari Dino 19.7 6 145.0 175 3.62 2.770 15.50 0 1 5 6
## Maserati Bora 15.0 8 301.0 335 3.54 3.570 14.60 0 1 5 8
## Volvo 142E 21.4 4 121.0 109 4.11 2.780 18.60 1 1 4 2
# Build the linear model
# lm(dependent variable ~ independent variable)
model_1 <- lm(mpg ~ wt, data = mtcars)
model_2 <- lm(mpg ~ hp, data = mtcars)
# Summary of the model
summary(model_1)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = mpg ~ wt, data = mtcars)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -4.5432 -2.3647 -0.1252 1.4096 6.8727
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 37.2851 1.8776 19.858 < 2e-16 ***
## wt -5.3445 0.5591 -9.559 1.29e-10 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 3.046 on 30 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.7528, Adjusted R-squared: 0.7446
## F-statistic: 91.38 on 1 and 30 DF, p-value: 1.294e-10
summary(model_2)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = mpg ~ hp, data = mtcars)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -5.7121 -2.1122 -0.8854 1.5819 8.2360
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 30.09886 1.63392 18.421 < 2e-16 ***
## hp -0.06823 0.01012 -6.742 1.79e-07 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 3.863 on 30 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.6024, Adjusted R-squared: 0.5892
## F-statistic: 45.46 on 1 and 30 DF, p-value: 1.788e-07
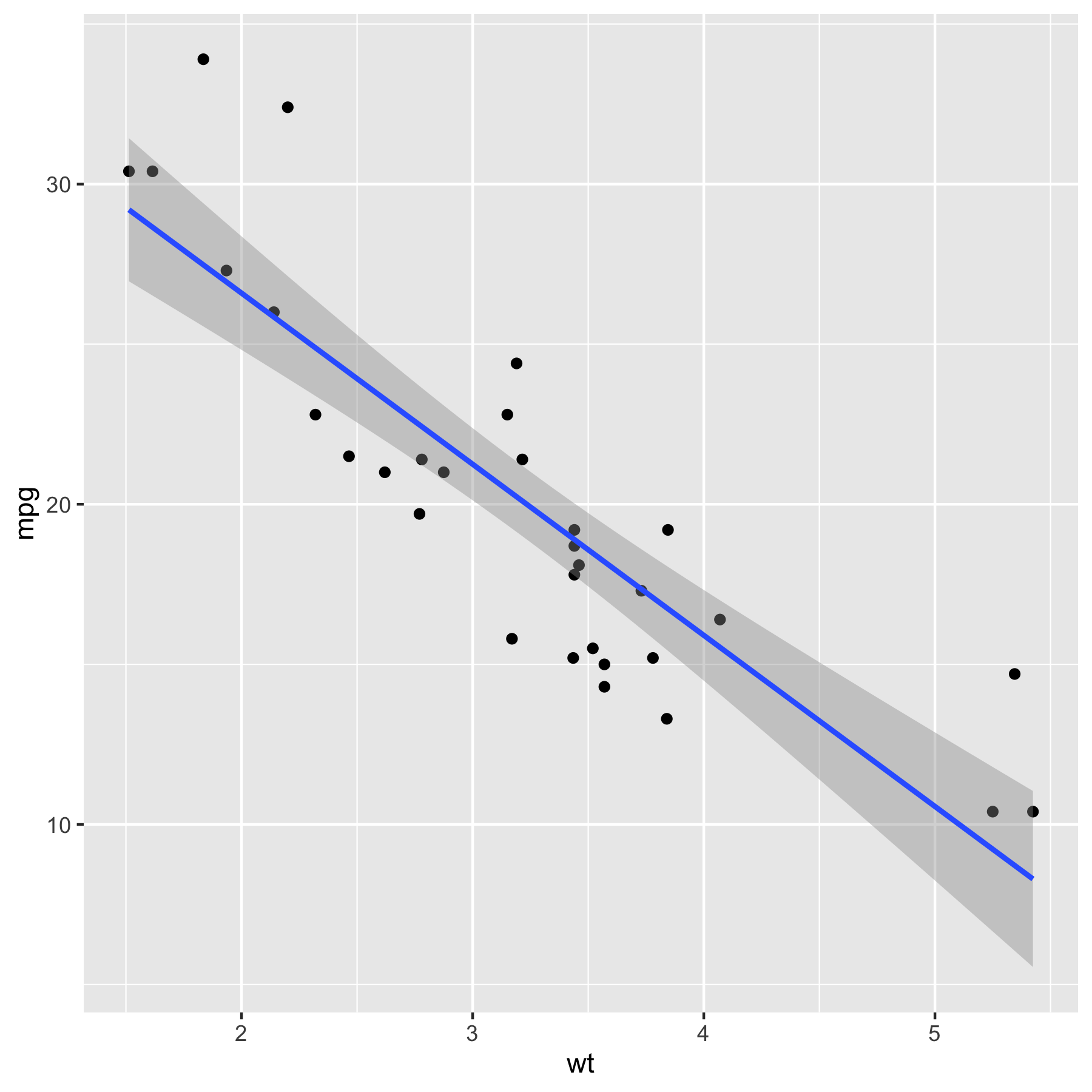
# Plotting the data points
mtcars %>%
ggplot(aes(x = wt, y = mpg)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = T)
# Build the multiple linear regression model
model_mult <- lm(mpg ~ wt + hp, data = mtcars)
# Summary of the model
summary(model_mult)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = mpg ~ wt + hp, data = mtcars)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -3.941 -1.600 -0.182 1.050 5.854
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 37.22727 1.59879 23.285 < 2e-16 ***
## wt -3.87783 0.63273 -6.129 1.12e-06 ***
## hp -0.03177 0.00903 -3.519 0.00145 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 2.593 on 29 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.8268, Adjusted R-squared: 0.8148
## F-statistic: 69.21 on 2 and 29 DF, p-value: 9.109e-12
A one unit increase in HP (horse power) is correlated with 0.03177 units lower in mile per gallon and is statistically significant at < 0.001 level. A one unit increase in WT (weight) is correlated with 3.877 units lower in mile per gallon and is statistically significant at 0.001 level.
Generating Predictions
After building a linear regression model, we can use it to make predictions. We’ll cover how to generate predictions for both the simple (bivariate) and multiple (multivariate) linear regression models.
Predictions with Simple Linear Regression
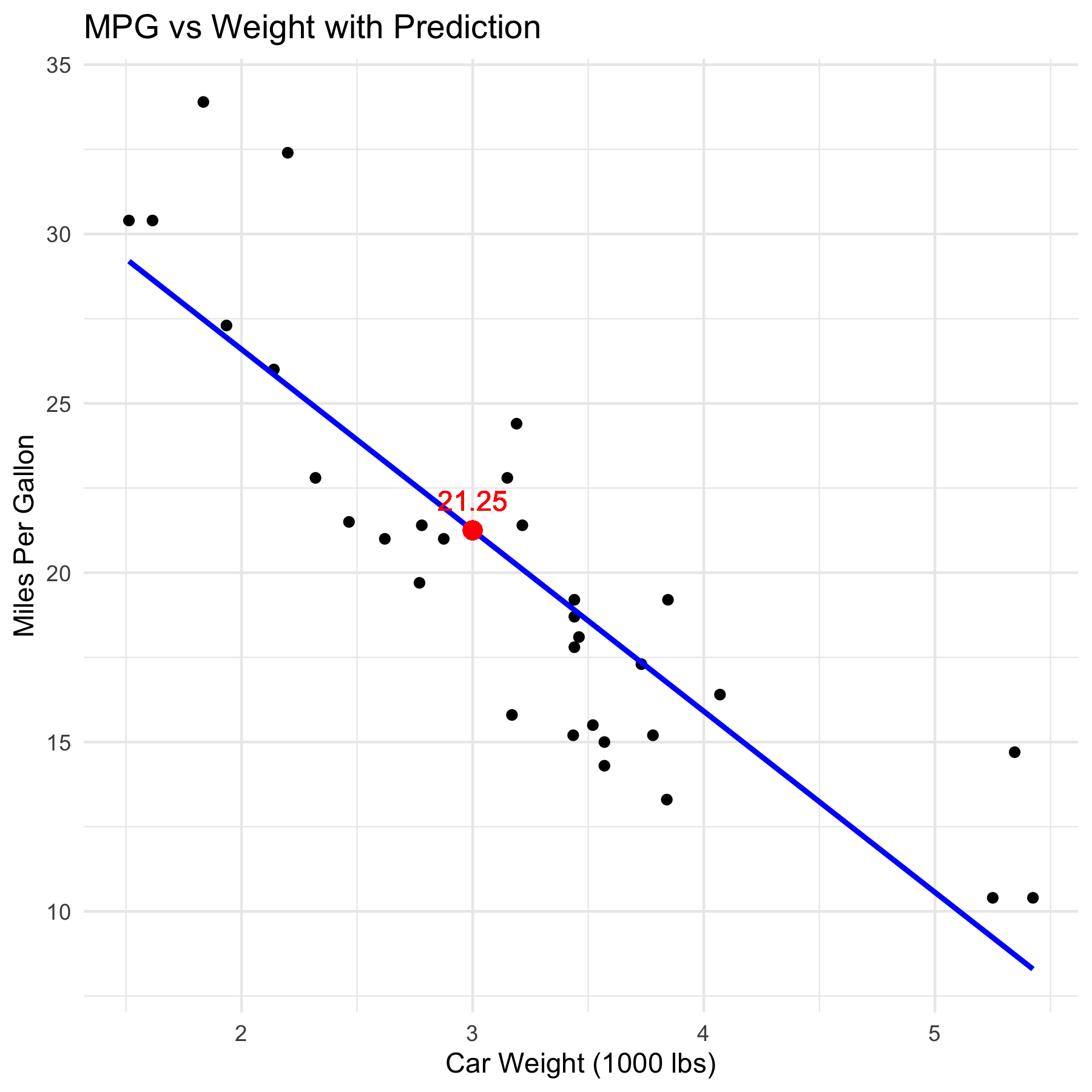
Using the model we created earlier (predicting mpg based on wt), let’s predict the mpg for a car that weighs 3,000 lbs.
new_data <- data.frame(wt = 3)
# Generate prediction
predicted_mpg <- predict(model_1, newdata = new_data)
# Output the prediction
predicted_mpg
## 1
## 21.25171
ggplot(mtcars, aes(x = wt, y = mpg)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", col = "blue", se = FALSE) +
geom_point(aes(x = new_data$wt, y = predicted_mpg), color = "red", size = 3) +
geom_text(aes(x = new_data$wt, y = predicted_mpg, label = round(predicted_mpg, 2)),
vjust = -1, color = "red") +
labs(title = "MPG vs Weight with Prediction",
x = "Car Weight (1000 lbs)",
y = "Miles Per Gallon") +
theme_minimal()